
Content
- Scabs on Dog Skin: How to Examine
- Dog Skin Sores: Canine Dermatitis
- canine atopic dermatitis
- canine seborrheic dermatitis
- Itchy dog and sores: canine scabies
- Dog wounds: leishmaniasis
- Dog wound: fungus in dogs
- Dog skin ulcers as a clinical sign of disease
- Dog skin wounds: canine pyoderma
- Wounds on the dog's skin due to poor nutrition or hygiene
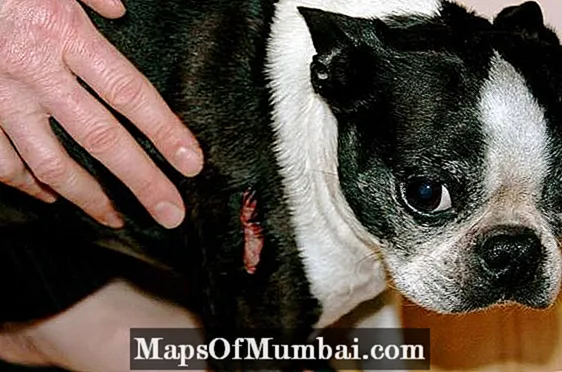
At scabs on the dog's skin indicate that the dog's health is compromised by a certain cause. We'll explain what the most common causes of scabs on the dog's dermis are, and we'll detail the main symptoms of each. Continue reading and find in this PeritoAnimal article important information about sores and scabs on the dog's skin.
Scabs on Dog Skin: How to Examine
A single scab on a dog's skin in a given area can be synonymous with a sore caused by excessive itching, a blow or a bite from another animal, while multiple scabs indicate that the original problem is much more serious.
Therefore, analyze the appearance of the crusts, their size and proximity is one of the first steps you should take to find out why your furry friend has skin sores. Also, pay attention to the dog's behavior, see if it shows signs of pain, has changed character, or has lost its appetite. Below, we show the most common causes, related symptoms, and possible solutions for dog's skin wounds.
Dog Skin Sores: Canine Dermatitis
Undoubtedly, one of the main causes of scabs on a dog's skin is canine dermatitis. Of all the existing types of dermatitis, two stand out from the others for producing this anomaly in the animal's dermis, they are canine atopic dermatitis and canine seborrheic dermatitis.
canine atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a skin condition that not only affects humans but can also manifest itself in animals. Although its exact cause is unknown, experts suggest that it is an intermittent skin disease, which appears in the presence of certain skin irritants and usually shows the first symptoms. in between 3 and 6 months of life, although an adult dog can also develop it.
In general, it usually produces intense itching in the dog, which results in frequent itching, sores on the dog's skin and consequent scabs. In addition, there is a clear reddening in certain areas of the animal's skin and even hair loss.
Canine atopic dermatitis is not curable, however, with proper care, it is possible to alleviate the symptoms to the point of almost completely eliminating them. It is recommended to adapt the dog's diet and choose a food rich in omega 3 fatty acids and linoleic acid, essential to keep the skin and fur in perfect condition. Learn more about the condition in the article Canine Atopic Dermatitis - Symptoms and Treatment.
canine seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis, also known as canine seborrhea, is another very common skin condition in dogs, mainly affecting the face, legs and trunk areas. This type of dermatitis occurs as a result of excessive sebum creation by the sebaceous glands. This fact is reflected in the appearance of yellowish or whitish scales attached to the fur, in small scabs on the dog's skin as a result of constant itching and an unpleasant or stronger body odor than usual.
This dermatitis is an inherited disease, which can be increased by stress, poor diet, excessive bathing or the use of inappropriate shampoo. As in the previous condition, there is no cure and its main treatment is to use an anti-seborrheic soap, as well as check the dog's diet and adapt it following the veterinarian's instructions to relieve the sores on the dog's skin.
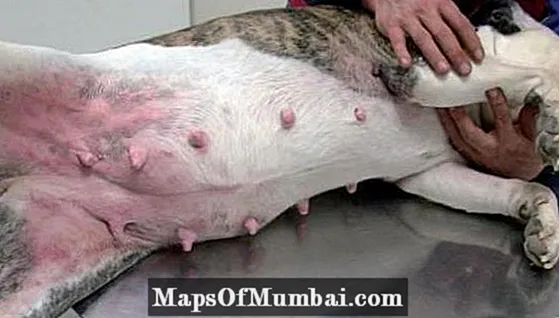
Itchy dog and sores: canine scabies
Canine mange is a type of skin infection caused by mites that settle on the animal's skin to feed on its keratin and sebum, reproducing quickly and distributing itself in large areas of the body. Although there are several types of mange, the most common in dogs are demodectic mange and sarcoptic mange. The first of these can be localized, acting mainly on the head, or generalized. The second usually appears on the trunk and legs.
In both types of mange, the dog is intensely itchy in the first stage of the disease, which results in frequent scratching and reddening of the skin. As the pathology progresses, a skin tightening, to the point of seeing cracks and scabs on the dog's skin. Thus, there is a partial or total loss of skin in the affected area, as well as bad smell and weight loss.
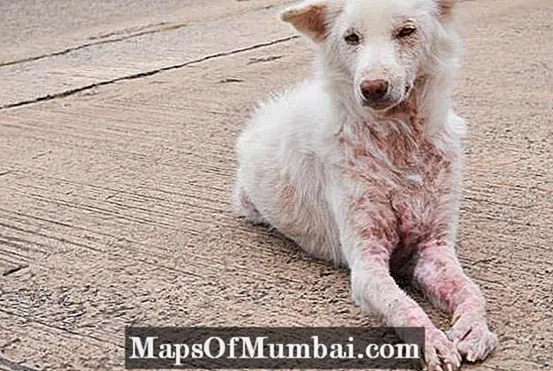
Dog wounds: leishmaniasis
Canine leishmaniasis is a chronic disease that has no cure, and treatment is based on symptom relief to improve the patient's quality of life. When infected, the dog goes through an incubation period that can last from 3 to 18 months, and begins to show the first symptoms when this terminal stage. In general, the dog suffers localized hair loss, with the legs, head and tail being the most affected parts, as well as considerable weight loss, thickening of the skin, sores and scabs.
As already mentioned, there is no cure for this condition, however, it is possible to guarantee a good quality of life through maintenance treatment, stipulated by the veterinarian.

Dog wound: fungus in dogs
There are several causes that can result in a topical fungal infection, such as prolonged exposure to damp environments, excessive bathing, immunosuppressive diseases, contact with other infected animals or hypersensitivity to environmental allergens.
Once infected, the dog will have frequent scratching as a result of intense itching, hair loss in areas affected by the fungus, skin inflammation, redness, dandruff and bed sores. In general, when it comes to fungi, the scabs on the dog's fur have a rounded shape and are located in specific areas.
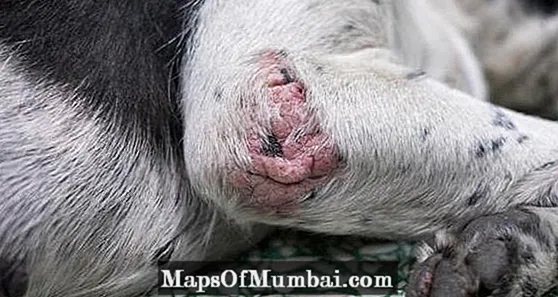
Dog skin ulcers as a clinical sign of disease
The dog's skin ulcers appear as a result of certain pathologies, so it is essential to go to the vet as soon as possible, as it explains why the dog presents scabs on the skin. Before naming the most common diseases that present them, it is important to know that the definition of an ulcer is a open skin lesion and inflamed, with secretion of pus or loss of other substances.
If it went unnoticed, over time it can appear as a scab or dog's skin wound, with some moisture or peeling only at the edges of the ulcer.
The most common conditions or diseases that cause ulcers are as follows:
- Burns;
- Irritating chemicals;
- Pyoderma;
- Scabies;
- Fungi;
- Skin cancer.
Dog skin wounds: canine pyoderma
In relation to the previous point, canine pyoderma is one of the main causes of ulcers, therefore, of crusts on the dog's skin, and it could not be missing from this list. Is skin disease caused by bacteria which usually appears as a simple infection, caused by flea infestation, or complex, produced as a result of another disease or disorder, such as seborrheic conditions, skin hypersensitivity or allergens, or leishmaniasis.
As it is a condition caused by bacteria, its proliferation occurs at high speed and can affect any part of the animal's body, with the head, trunk and legs being more common. Thus, the main symptoms of canine pyoderma are intense itching, skin redness, inflammation, sores and scabs. If the necessary attention is not given, the injuries caused tend to worsen and present areas with shocking crusts, sores on the dog's skin with pus or bleeding.

Wounds on the dog's skin due to poor nutrition or hygiene
Not all the causes that explain why a dog has crusts on the skin are related to the development of diseases, as sometimes the reason is much simpler and is found in the animal's daily habits. In that regard, quality food is the basis of a healthy life. and a strong immune system.
If the dog follows a diet low in protein, vitamins and essential acids, this will be reflected in the condition of the coat and skin, showing a coat opaque, rough, a dry, cracked or crusted dermis. Thus, it is recommended to pay careful attention to the composition of the food to choose one that meets the specific needs of the dog in question or, if a homemade diet is followed, consult the veterinarian to propose a balanced diet.
On the other hand, as we saw in the previous sections, inadequate hygiene can lead to the development of pathologies that trigger scabs on the dog's skin, among other symptoms. Within the term "inappropriate", the following habits are found:
- excessive bathing the dog. The ideal is to bathe the dog every month or every month and a half, or do it when it is really dirty.
- Using an incorrect shampoo. In cases of dermatitis or skin disorders, the use of a common shampoo can make the problem worse, aggravating the clinical picture. For this reason, the condition of the animal's skin should be carefully checked to recognize any signs and visit the specialist.
- Use an inappropriate brush. Depending on the type of fur of the dog, you should use a brush or another, because the use of an inappropriate brush can end up producing sores on the skin. Likewise, the coat must always be brushed in the direction of the coat. Check out our article on brush types and how to properly brush your dog's fur to learn more.
Finally, consider the importance of making regular visits to the veterinarian to identify any abnormalities and treat them in time, and consult a specialist in the presence of any symptoms or abnormalities.

This article is for information purposes only, at PeritoAnimal.com.br we are not able to prescribe veterinary treatments or perform any type of diagnosis. We suggest that you take your pet to the veterinarian in case it has any type of condition or discomfort.
If you want to read more articles similar to Sores and scabs on the dog's skin, we recommend that you enter our Skin Problems section.