
Content
- White feces in dogs due to feeding
- And will they stop being white and hard with time?
- acolic stools
- Dog with white feces with mucus
- White dog defecating by parasites

The observation of our dog's feces is possibly one of the simplest and cheapest ways to control his health status and anticipate any possible changes. When we go to the vet, the first question on a control review is probably "how are your stools?” And the variation in color from our dog's usual pattern often causes us a lot of apprehension.
This article by PeritoAnimal about most common causes of white stools in dogs is intended to shed some light on this more or less unusual coloration in the stool, and to encourage you to check the consistency and appearance of your dog's droppings daily.
White feces in dogs due to feeding
THE switch to a raw meat and bones diet it can lead to hard white stools that break like chalk in your hands when we try to catch you. The reason for this color and hardness is the presence of calcium that is found in the bones that our dog eats. Sometimes the amount of bone is excessive and we may find our dog having difficulty defecating even though he tries repeatedly. This constant desire to defecate is called ’urgency’, and if we choose these diets, we should consult a specialist who will advise us on their follow-up to facilitate intestinal transit and not cause anal fissures or obstructions.
Does that mean I should stop this diet?
In principle, if we allow ourselves to be guided by experts and the dog responds appropriately to the new diet, we should just manage that specific inconvenience. To avoid the worrying presence of these hard white feces in the dog, we can choose:
- add more fiber in the diet, with products such as pumpkin or use asparagus.
- Reduce the amount of bone, vary the type or choose to use them on certain days of the week.
- Try using pro/prebiotics to promote intestinal fermentation and adaptation to a new diet based on live bacteria like Faecium Enterococcum or lactobacillus and other substrates for existing beneficial bacteria to flourish, such as inulin, a disaccharide.
- Use during the first few days to adapt a similar intestinal lubricant that humans in occasional constipation situations can help, such as liquid paraffin (with a slightly unpleasant taste), or even provide a couple of tablespoons of olive oil to every 12 hours until everything is normalized, correcting the dose according to the results. In this sense, we recommend that you consult our article on the benefits of oil for dogs, in order to expand your information and discover all its uses.
Using other drugs that we usually have on hand for these situations is not suitable, although it may seem like it will be good for our dog, because before stimulating intestinal motility, we must ensure that these too hard stools have not been compressed to form a fecalite. or fecaloma (literally, stone-like stools) and resulted in an intestinal obstruction.
The color of the feces is still a reflection of what the dog ingests, it is not always a decision of the owner. Thus, in field dogs, with free access to farms and other territories, we can find these hard white feces without waiting for it. Even though we feed it regularly, many dogs with free time and enough territory steal the eggs or eat carrion, including bones and feathers, so the feces sometimes, to our displeasure, tell us their customs while we do not watch them. This extra calcium, coming from the eggshell and the skeletons of its prey, can result in hard white droppings in the dog.
In dogs that tend to defecate in places we don't see, or are never sure what they're doing or eating, it's vital that we check for feces and look for any abnormalities. If you need to force him to stay three days at home or in the garage to check, this information can prevent intestinal obstructions before it's too late, for example.
And will they stop being white and hard with time?
The color of the feces of dogs that feed on homemade diets depends on the amount of food they ingest, and on what day they do it and you can notice small variations in color and consistency during the week. Generally the white color will remain white, with variations, and the hardness will be corrected depending on what is most appropriate for the dog with all the advice that the experts give us, but almost always you will expect less stool, more compact and lighter than in animals fed with feed.

acolic stools
Sterecobilin is the brown pigment formed by bilirubin and gives color to stools. If for any reason the formation and transport of bilirubin is altered, it is inevitable that the stool will appear in a whitish gray color, which is called acolic stool.
And what can cause a lack of stercobilin?
there may be a liver disorder, in which case the liver is unable to carry out its functions. Among them is the formation of bilirubin from erythrocyte degradation products. As a result, this pigment will not accumulate in the gallbladder and will not be evacuated into the duodenum with the rest of the bile substances after each meal, so stercobilin cannot form from it, and the stool has its usual color. Some causes of liver failure that can be found in dogs are:
- liver neoplasm: primary or secondary tumors (eg a breast or bone tumor metastasis).
- congenital alteration (birth) at the level of hepatic vascularization.
- acute hepatitis: liver inflammation, for example, due to ingestion of toxic substances, or of viral origin (canine hepatitis virus), or bacterial (leptospirosis).
- Cirrhosis: liver degeneration as a result of prolonged illness, eg subacute hepatitis sustained over time. It is the end result of many liver diseases that may have gone unnoticed by the owner and the veterinarian due to the great compensatory capacity of this organ.
- pancreatitis: inflammation of the pancreas.
Likewise, any alteration in the transport of bilirubin can cause a deficit of bilirubin in the gallbladder (rare in dogs), obstruction of the bile duct by some abdominal mass that compresses and prevents the bile from evacuating... in these cases of failure or absence of evacuation of bile into the duodenum, stools often present with steatorrhea (presence of fat in the stool, which causes a pasty appearance) as bile acids are needed to absorb fat and since acids are lacking, the fat is eliminated totally in the stool. At white and soft stools in dogs, as fat, they are often a sign of a liver or pancreatic disease.
And how to detect these problems?
The liver is usually slow to alert you to your condition, unless it is a hyperacute disease. Thanks to its aforementioned reserve capacity, it can guarantee functions even when a large percentage of its extension is affected. But if our dog has any or all of the following symptoms, it may be time to go to the appointment:
- Performs frequent bowel movements, with colic and/or pasty stools.
- Presents biliary vomiting.
- Itching of unknown origin.
- Jaundice
- Anorexia or hyporexia (eats, but much less).
- Increased water intake.
- Abdominal distension (ascites) or pain when touched, exercise intolerance...
A series of laboratory tests, including blood count, biochemistry and total protein, in principle, and possibly panel clotting, as well as a detailed clinical history carried out by the specialist with our help, is the key to detecting the exact origin of the white feces on our dog. However, and as liver enzymes are not always altered as expected by symptoms, imaging tests (plates, ultrasound...) are almost always necessary.

Dog with white feces with mucus
Sometimes the stools are normal in color but look like wrapped in a white, gelatinous tissue, which leads us to think that this is your color. But if we try to undo them, we can see that, in reality, it is a kind of bag that covers them completely or just in one area.
To avoid this specific gut irritation, we should make dietary changes gradually, help with probiotics if necessary, and deworm it regularly or with the appropriate products as advised by our veterinarian.
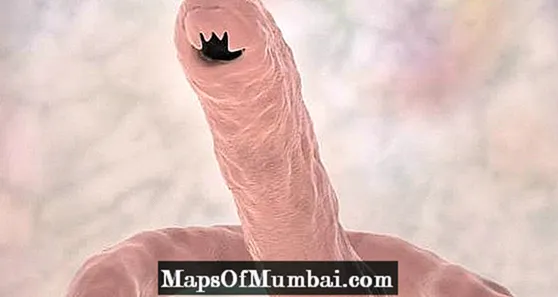
White dog defecating by parasites
Dogs are sometimes so parasitized intestinally that at the beginning of their deworming plan scheduled by our veterinarian, we are alarmed to see that their stools are practically white. Normally, this is due to the appearance of numerous nematodes (worms) already dead and sometimes fragmented, attached to the fecal surface, and we can even find some living and mobile. It all depends on how the product we use for deworming works, as some force the parasite out of the intestinal wall, others kill it directly when they absorb it into the blood or through its integument, etc.
If our dog has several tapeworms, usually of the type Dipylidium caninum, the massive elimination of gravidarum proglottids to the outside can make us observe feces filled with a kind of white rice grains. They can become so numerous in relatively small fecal matter that we confuse their presence with really white stools if we don't get close enough and collect them to see what color this color is due to. For more information about this type of parasite, don't miss our article "Intestinal parasites in dogs - symptoms and types".
Don't you think it's important to look at what the stool looks like and collect it almost without looking at it? The saying that "we are what we eat" is very true, and feces can tell us about our dog's health. Also, appearances can sometimes be deceiving, reason all the more to check that everything is in order when they when the dog relieves himself in his daily walks.
This article is for information purposes only, at PeritoAnimal.com.br we are not able to prescribe veterinary treatments or perform any type of diagnosis. We suggest that you take your pet to the veterinarian in case it has any type of condition or discomfort.