
Content
- What are decomposing beings
- Decomposers in the food chain
- Importance of decomposers in nature
- Types of decomposing beings
- Detritivorous beings
- scavengers
- coprophagous beings
- Decomposing animals
- Examples of decomposing animals
- Examples of Detritivorous Animals
- Example of scavenger animals
- Examples of dung animals

In any ecosystem, just as there are food chains where we find vegetable producing organisms (there are no animal producers) and consuming animals, there is also a detritivorous food chain, whose objective is to transform all organic matter, from the other food chain, into inorganic matter, making these compounds absorbable again by plants. Within this chain we find decomposing or detritive beings, some of which are decomposing animals, although most of them are fungi or bacteria.
In this article by PeritoAnimal, we will see what decomposers are and the importance of their role in the ecosystem.
What are decomposing beings
The decomposing beings are heterotrophic organisms that feed on organic matter in the process of decomposition or waste from other animals, such as faeces. These organisms are also called saprophages. Decomposition is a natural process necessary in ecosystems for the renewal of matter and energy. It is performed by a multitude of organisms, many of which are decomposing bacteria or chemoorganotrophic organisms because they obtain energy through chemical reactions, using decaying organic matter as a substrate.
Another very important group of organisms are the decomposing fungi, both microscopic and macroscopic. Finally, although they are usually at the beginning of the detritivorous chain, we find the decomposing animals, with scavengers being an important group.

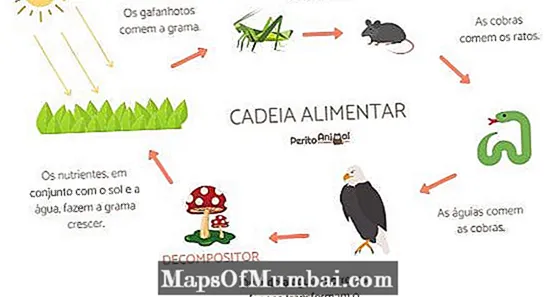
Decomposers in the food chain
In any ecosystem, there is a food chain where it is possible to find producers, consumers and decomposers. The latter act after the death of producer beings and various consumer beings.
Organic matter resulting from producers and consumers (stool, biomass and other waste excreted by the body) serves as food for decomposers like fungi and bacteria, being your source of energy and nutrients.
Importance of decomposers in nature
The role of decomposers for the ecological balance of an ecosystem is fundamental. They play an extremely important role in the ecological balance, since they transform organic matter into inorganic matter, thus returning nutrients to the environment. This will allow these nutrients to be reused by other beings that will produce new organic matter.
In short, decomposing beings are in charge of recycle organic matter in the food chain.
Types of decomposing beings
There are mainly three types of decomposers, classified according to origin of organic matter decomposing, whether it is a corpse or parts of it, dead plant matter or feces. Accordingly, the types we find are:
Detritivorous beings
They are the ones who feed on the debris or from the vegetable parts that accumulate in the soil, such as leaves, roots, branches or fruits, and which after decomposition end up forming humus, which is a soil very rich in organic matter.
scavengers
These organisms feed on the corpses or body parts of decaying animals. Normally, this action is initiated by bacteria that facilitate the assimilation of organic matter to decomposing animals.
coprophagous beings
They are organisms, mostly fungi and decomposing animals, that feed on organic matter that can still be assimilated from feces.
Decomposing animals
The definition of decomposing animals is none other than:
Living beings belonging to the animal kingdom that feed on decaying organic matter.
We found decomposing animals in both the invertebrate and vertebrate groups. Among the first, perhaps the most important group are insects, of many types, such as flies, wasps or beetles. Where do we find more examples of decomposing vertebrate animals in groups of mammals and birds.
On the other hand, the abundance of this type of animals varies with the weather. For example, decomposing animals in the desert are rare, only a few invertebrates. It is in humid places where we can find the greatest diversity of these organisms, being the decomposing animals of the forest the ones with the greatest diversity.
Examples of decomposing animals
Below, we present a list with examples of decomposing animals sorted by type:
Examples of Detritivorous Animals
- The earthworms (Family Lubricidae), play a key role in humus formation.
- Gastropods (Mollusks, Lemas and Snails). Many of these animals also feed on live plants, which causes some to become pests.
- omnicides or woodworms (Omnicides Suborder).
Example of scavenger animals
- Diptera or flies (Families Sarcophagidae, Calliphoridae, Phoridae or Muscidae). At forensic science these animals and beetles are taken into account to determine the time of death.
- Coleoptera or beetles (Families Silphidae or Dermestidae)
- hyenas (Family Hyaenidae). Some ecologists would not include carrion animals as part of the scavenger fauna, but the truth is that they play an important role in the decomposition of corpses.
- vultures (Family Accipitridae and Cathartidae)
Examples of dung animals
- Coleoptera or Beetles (Families Scarabaeidae, Geotrupidae and Hybosoridae). This includes the famous dung beetles.
- Diptera or flies (Families Calliphoridae, Sarcophagidae or Muscidae). The green fly (Phaenicia sericata) is very recognizable about animal droppings.
- Egyptian Vulture (Neophron percnopterus). In addition to being a scavenger, it supplements its diet with cow feces to absorb the carotenoids (vegetable pigment) that give its beak its striking color.

If you want to read more articles similar to Decomposing beings: what they are, types and examples, we recommend that you enter our Curiosities section of the animal world.