
Content
- prehistoric animals
- Titanoboa (Titanoboa cerrejonensis)
- Emperor crocodile (Sarcosuchus imperator)
- Megalodon (Carcharocles megalodon)
- 'Birds of terror' (Gastornithiformes and Cariamiformes)
- Arthropleura
- Brazilian prehistoric animals
- South American Sabertooth Tiger (Smilodon populator)
- Prionjuice (Prionosuchus plummeri)
- Chiniquodon (Chiniquodon theotonicus)
- Titan of Uberaba (Uberabatitan ribeiroi)
- Caiuajara (Caiuajara dobruskii)
- Brazilian Giant Sloth (Megatherium americanum)
- Amazon Tapir (Tapirus rondoniensis)
- Giant Armadillo (Gliptodon)
- Giant freshwater turtle (Stupendemys geographicus)

Talking about prehistoric animals is immersing yourself in a world so familiar and so unknown at the same time. Dinosaurs, for example, that dominated planet Earth millions of years ago inhabited the same planet and another ecosystem with different continents. Before and after them there were millions of other species that, in many cases, there remains a fossil to tell a story and challenge the human paleontological capacity to unravel them. Proof of this are these 15 prehistoric animals that we selected in this post by PeritoAnimal and its sublime characteristics.
prehistoric animals
When we talk about prehistoric animals, it is normal that dinosaurs come to mind, their magnificence and Hollywood fame, but before and after them, there were other prehistoric creatures as or more impressive as them. Check out some of them:
Titanoboa (Titanoboa cerrejonensis)
inhabitant of Paleocene period (after the dinosaurs), a detailed description of Titanoboa is enough to stir the imagination: 13 meters long, 1.1 meters in diameter and 1.1 ton. This was one of the greatest species of snake known on earth. Their habitat was humid, hot and swampy jungles.

Emperor crocodile (Sarcosuchus imperator)
This giant crocodile lived in North Africa 110 million years ago. His studies indicate that it was a crocodile of up to 8 tons, 12 meters long and a powerful bite of 3 tons of force, which helped him to capture giant fish and dinosaurs.

Megalodon (Carcharocles megalodon)
that kind of giant shark it's a two prehistoric marine animals it lived at least 2.6 million years ago, and its fossils have been found on different continents. Regardless of the origin of the species, it is impossible not to be impressed by its description: between 10 and 18 meters in length, up to 50 tons and sharp teeth of up to 17 centimeters. Discover other shark types, species and characteristics.

'Birds of terror' (Gastornithiformes and Cariamiformes)
This nickname does not refer to a species, but to all prehistoric carnivorous birds taxonomically classified in the orders Gastornithiformes and Cariamiformes. The large size, inability to fly, large beaks, strong claws and paws and up to 3 meters tall are common features of these carnivorous birds.

Arthropleura
Among prehistoric animals, illustrations of this arthropod cause shivers in those who do not get along with insects. That's because the o arthropleura, O largest terrestrial invertebrate What is known is a species of giant centipede: 2.6 meters long, 50 cm wide and about 30 articulated segments that allowed it to move quickly through the tropical forests of the Carboniferous period.

Brazilian prehistoric animals
The territory that is now called Brazil was the stage for the development of many species, including dinosaurs. Studies show that dinosaurs may have appeared in the region that is now defined as Brazil. According to PaleoZoo Brazil [1], a catalog that brings together extinct vertebrates that once inhabited the Brazilian territory, the great Brazilian biodiversity currently does not represent even 1% of what has already existed. These are some of the Brazilian prehistoric animals most amazing listed:
South American Sabertooth Tiger (Smilodon populator)
The South American Sabertooth Tiger is estimated to have lived at least 10,000 years between South and North America. Its popular name is given precisely by the 28 centimeter teeth that it adorned with its robust body, which could reach 2.10 meters in length. It is one of biggest cats that one has knowledge of existence.

Prionjuice (Prionosuchus plummeri)
Alligator? No. This is one of the Brazilian prehistoric animals known for being the biggest amphibian that ever lived, more specifically about 270 million years ago, in the portion of land that is today the Brazilian northeast. It is supposed that this prehistoric Brazilian animal with aquatic habits could reach up to 9 meters in length and was a feared predator of aquatic ecosystems at that time.

Chiniquodon (Chiniquodon theotonicus)
It is known that the Chiniquodon had a mammalian anatomy, size of a large dog and inhabited the present south of South America and had ferocious and carnivorous habits. The species whose evidence was found in Brazil is called Chiniquodon brasilensis.

Stauricosaurus (Staurikosaurus pricei)
This may have been the first species of dinosaur in the world. At least it is one of the oldest known. the fossils of Staurikosaurus pricei were found in Brazilian territory and show that it measured 2 meters in length and less than 1 meter in height (about half the height of a man). Apparently, this dinosaur hunted terrestrial vertebrates smaller than itself.

Titan of Uberaba (Uberabatitan ribeiroi)
Tiny, just not. The Uberaba Titan is the largest Brazilian dinosaur whose fossils were found, as its name indicates, in the city of Uberaba (MG). Since its discovery, it is considered the largest known Brazilian dinosaur. It is estimated that it measured 19 meters in length, 5 meters in height and 16 tons.
Image:Reproduction/http://thumbs.dreamstime.com/x/uberabatitan-dinasaur-white-was-herbivorous-sauropod-dinosaur-lived-cretaceous-period-brazil-51302602.webp

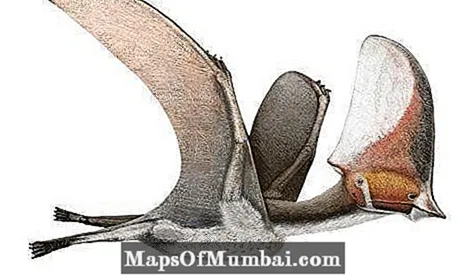
Caiuajara (Caiuajara dobruskii)
Among Brazilian prehistoric animals, the Caiuajara fossils indicate that this carnivorous species of flying dinosaur (pterosaur) could have a wingspan of up to 2.35 meters and weigh up to 8 kg. Studies of the species indicate that it inhabited desert and sandy areas.
Brazilian Giant Sloth (Megatherium americanum)
Megatherium or Brazilian giant sloth is one of the Brazilian prehistoric animals that arouses curiosity for its appearance of the sloth we know today, but weighing up to 4 tons and measuring up to 6 meters in length. It is estimated that it inhabited Brazilian surfaces 17 million years ago and disappeared some 10,000 years ago.

Amazon Tapir (Tapirus rondoniensis)
Relative of the Brazilian tapir (Tapirus terrestris), which is currently considered the largest Brazilian terrestrial mammal , the Amazonian tapir is a mammal from the Quartenary period that is already extinct in the Brazilian fauna. Fossils and animal studies reveal that it was very similar to the current Brazilian tapir with differences in skull, dentition and crest size. Even so, there are controversies[2]and whoever claims that the Amazon tapir is actually just a variation of the Brazilian tapir and not another species.

Giant Armadillo (Gliptodon)
Another of the Brazilian prehistoric animals that impresses is the gliptodon, a prehistoric giant armadillo that inhabited South America 16 thousand years ago. Paleontological studies indicate that this species had a carapace like the armadillo we know today, but it weighed a thousand kilos and was very slow, with a herbivorous diet.

Giant freshwater turtle (Stupendemys geographicus)
According to studies, this giant tortoise is one of the Brazilian prehistoric animals that inhabited the Amazon when the Amazon River region with the Orinoco was still a giant swamp. According to fossil studies, the Stupendemys geographicus it could have the weight of a car, horns (in the case of males) and lived at the bottom of lakes and rivers.

If you want to read more articles similar to Prehistoric animals: characteristics and curiosities, we recommend that you enter our Curiosities section of the animal world.
Advices- Many of the images presented in this article are the result of paleontological constitutions and do not always represent the exact form of the prehistoric species described.