
Content
- Insect classification
- Odonata
- orthopter
- Examples of Orthopteran Insects
- isoptera
- Examples of Isoptera insects
- hemipterus
- Examples of Hemiptera Insects
- Lepidoptera
- Examples of lepidopteran insects
- Coleoptera
- Diptera
- Examples of Diptera Insects
- Hymenoptera
- Examples of hymenopteran insects
- Types of Wingless Insects
- Examples of Apterous Insects
- other types of insects

Insects are hexapod arthropods, so their bodies are divided into the head, thorax, and abdomen. Also, all have six legs and two pairs of wings that protrude from the chest. However, as we will see later, these appendices vary according to each group. In fact, together with antennas and mouthparts, it is possible to easily differentiate the different types of insects that exist.
This group of animals is the most diverse and contains about a million species. However, it is believed that most have not yet been discovered. Want to know more about insects? In this PeritoAnimal article, we will explain what the types of insects, their names, features and more.
Insect classification
Due to their enormous diversity, the classification of insects includes a large number of groups. Therefore, we will explain about the most representative and known types of insects. These are the following orders:
- Odonata;
- Orthopter;
- Isoptera;
- Hemiptera;
- Lepidoptera;
- Coleoptera;
- Diptera;
- Hymenoptera.
Odonata
Odonata are one of the most beautiful insects in the world. This group includes more than 3,500 species distributed throughout the world. They are dragonflies (infraorder of Anisoptera) and damsels (suborder of Zygoptera), predatory insects with aquatic offspring.
Odonata have two pairs of membranous wings and legs that serve to capture prey and grasp the substrate, but not to walk. Their eyes are compound and appear apart in maidens and close together in dragonflies. This feature allows you to differentiate them.
Some types of insects that belong to this group:
- Calopterix virgo;
- Cordulegaster boltoni;
- Emperor Dragonfly (Anax imperator).

orthopter
This group is that of locusts and crickets that total more than 20,000 species. Although they are found almost all over the world, they prefer the warmer regions and seasons of the year. Both young and adults feed on plants. They are ametabolic animals that do not undergo metamorphosis, although they do undergo some changes.
We can easily differentiate these types of animals because their forewings are partially hardened (tegminas) and their hind legs are large and strong, perfectly adapted for jumping. They usually have green or brown colors that help them to camouflage themselves in their surroundings and hide from the large number of predators that chase them.
Examples of Orthopteran Insects
Some examples of grasshoppers and crickets are:
- Hope or Green Cricket (Tettigoria viridissima);
- European mole cricket (Gryllotalpa gryllotalpa);
- Euconocephalus thunbergii.

isoptera
The termite group includes about 2,500 species, all of which are very abundant. These types of insects usually feed on wood, although they can eat other plant substances. They live in large termite mounds built in wood or in the ground and have castes that are much more complex than we know.
Its anatomy depends on the different castes. However, they all have large antennae, locomotive legs, and an 11-part abdomen. As for the wings, they only appear in the main players. The rest of the castes are apter insects.
Examples of Isoptera insects
Some species of termites are:
- Wet wood termite (Kalotermes flavicollis);
- Dry wood termite (cryptotermes brevis).

hemipterus
These types of insects refer to bed bugs (suborder heteropter), aphids, scale insects and cicadas (Homoptera). In total they are more than 80,000 species, being a very diverse group that includes aquatic insects, phytophagous, predators and even hematophagous parasites.
Bedbugs have hemiéliters, meaning their forewings are hard at the base and membranous at the apex. However, homopters have all their membranous wings. Most have well-developed antennas and a bite-sucking mouthpiece.
Examples of Hemiptera Insects
Some examples of these types of insects are:
- Barbers (Triatoma infestans);
- Broad bean louse (aphis fabae);
- Cicada orni;
- Carpocoris fuscispinus.

Lepidoptera
The lepidopteran group includes more than 165,000 species of butterflies and moths, it is one of the most diverse and abundant types of insects. Adults feed on nectar and are pollinators, while larvae (caterpillars) are herbivores.
Among its characteristics stand out the complete metamorphosis (holometabolic), its membranous wings covered with scales and its proboscis, a very elongated mouthpart that is curled when they are not feeding.
Examples of lepidopteran insects
Some species of butterflies and moths are:
- Atlas moth (atlas atlas);
- Emperor moth (Thysania agrippina);
- Skull Boboleta (Atropos Acherontia).
Coleoptera
It is estimated that there are more than 370,000 species known. Among them, there are insects as different as the golden cow (Lucanusdeer) and ladybirds (Coccinellidae).
The main characteristic of this type of insect is that its forewings are completely hardened and are called elytra. They cover and protect the back of the wings, which are membranous and are used for flying. In addition, the éliters are essential to control the flight.

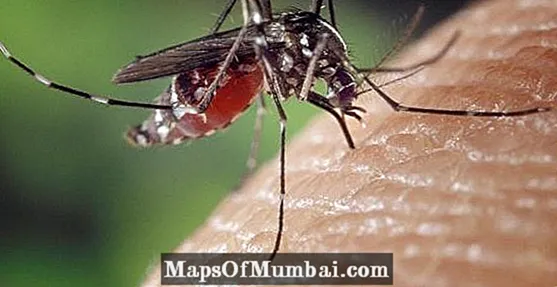
Diptera
They are flies, mosquitoes and horseflies that gather more than 122,000 species distributed around the world. These insects undergo metamorphosis during their life cycle and adults feed on liquids (nectar, blood, etc.), as they have a mouth-sucking and lip system.
Its main feature is the transformation of its hind wings into structures known as rocker arms. The forewings are membranous and flap them to fly, while the rockers allow them to maintain balance and control the flight.
Examples of Diptera Insects
Some types of insects belonging to this group are:
- Asian Tiger Mosquito (Aedes albopicus);
- tsetse fly (genus Glossine).
Hymenoptera
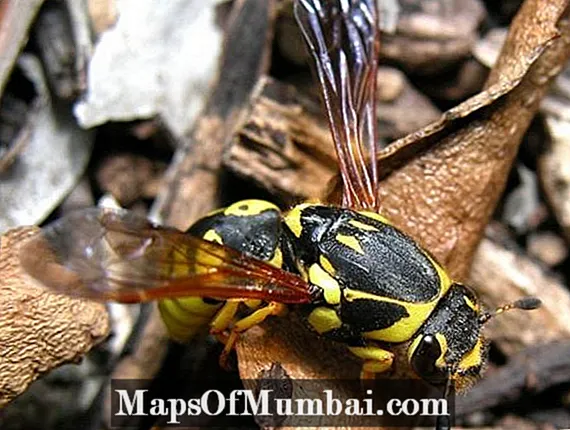
Hymenoptera are ants, wasps, bees and symphytes. It's the second largest group of insects, with 200,000 described species. Many species are social and organized into castes. Others are solitary and often parasitoid.
Except for the symphytes, the first segment of the abdomen is joined to the thorax, which allows them great mobility. Regarding the mouthparts, this is a chewer in predators such as wasps or lip sucker in those that feed on nectar, such as bees. All of these types of insects have powerful wing muscles and a highly developed glandular system that allows them to communicate very efficiently.
Examples of hymenopteran insects
Some species found in this group of insects are:
- Asian Wasp (velutine wasp);
- Potter Wasps (Eumeninae);
- Masarinae.

Types of Wingless Insects
At the beginning of the article, we said that all insects have two pairs of wings, however, as we have seen, in many types of insects these structures have been transformed, giving rise to other organs, such as elytra or rocker arms.
There are also apter insects, that is, ones that do not have wings. It is the result of your evolutionary process, this is because the wings and the structures necessary for their movement (wing muscles) require a lot of energy. Therefore, when they are not needed, they tend to disappear, allowing energy to be used for other purposes.
Examples of Apterous Insects
The best known insects are the majority of ants and termites, from which wings only appear in the reproductive individuals that leave to form new colonies. In this case, the determinant of whether the wings appear or not is the food that is provided to the larvae, that is, the genes that encode the appearance of the wings are present in their genome, but depending on the type of food during development, their expression is suppressed or active.
Some species of hemiptera and beetles have their wings transformed and permanently attached to their bodies so that they cannot fly. Other types of insects, such as the order Zygentoma, do not have wings and are true insects. One example is moths or silver pieixinho (Lepisma saccharina).
other types of insects
As we said before, there are several types of insects that it is very difficult to name each one of them. However, in this section, we will explain in detail about other less abundant and more unknown groups:
- Dermaptera: also known as scissors, are insects that live in wet areas and have appendages as a staple at the end of the abdomen.
- Zygentoma: they are apterous, flat and elongated insects that flee from light and dryness. They are known as "moisture bugs" and among them are the silver bugs.
- Blattodea: are cockroaches, insects with long antennae and partially hardened wings that are more developed in males. Both have appendages at the end of the abdomen.
- Cloak: praying mantises are animals perfectly adapted to predation. Its forelegs are specialized in abducting prey and have a great ability to mimic their surroundings.
- Phthiraptera: are lice, a group that includes more than 5,000 species. All are hematophagous external parasites.
- Neuropter: includes various types of insects such as lion ants or lacewings. They have membranous wings and most are predators.
- Shipphonaptera: they are the dreaded fleas, blood-sucking external parasites. Its mouthpiece is a chopper-sucker and its hind legs are very developed for jumping.
- Trichoptera: this group is largely unknown, although it includes more than 7,000 species. They have membranous wings and their legs are very long, like a mosquito's. They stand out for the construction of “boxes” to protect their larvae.
If you want to read more articles similar to Types of insects: names and characteristics, we recommend that you enter our Curiosities section of the animal world.